Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Phenotype, Genotype, Genetic Trait, First Filial Generation, Second Filial Generation, Homozygous Trait, Heterozygous Trait, Back Cross, Dominant Trait, Recessive Trait, Mendel's Experiment, Monohybrid Cross, etc.
Important Questions on Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Which of the following law of inheritance has not been given by Mendel:
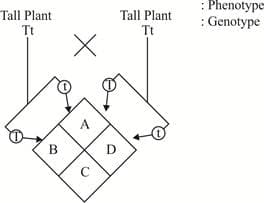
Look at the given diagram and answer the following question :
Identify the phenotypic ratio of A, B, C, D.
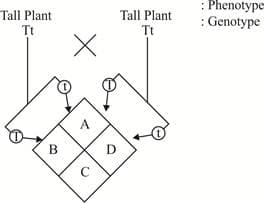
Look at the diagram given below and answer the following question :
Identify the genotypes of A, B, C, D.
You are given tall pea plants with yellow seeds whose genotypes are unknown. It was crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. The progeny obtained has equal ratio of tall and dwarf plants and equal proportion of green and yellow seeds. The genotype of the first plant is:
When a violet flower producing plant was crossed with white flower producing plant, the progeny obtained had all violet flower.
The genotype of first parent was homozygous or heterozygous:
A homozygous tall pea plant with yellow seeds is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. The phenotypic ratio of its F2 plants is 9:3:3:1. It is representing:
A plant of Antirrhinum majus with red flowers was crossed with another plant of the same species with white flowers. The plants of the F1 generation bore pink flowers. The pattern of inheritance is exhibiting:
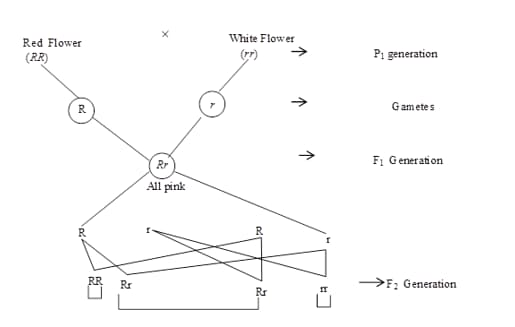
A homozygous tall pea plant with yellow seeds is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. The phenotypic ratio of its F2 plants would be:
A plant of Antirrhinum majus with red flowers was crossed with another plant of the same species with white flowers. The plants of the F1 generation bore pink flowers. The pattern of inheritance is exhibiting:
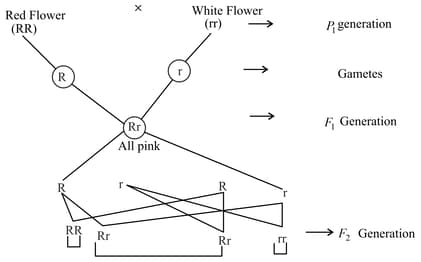
If a homozygous tall plant is crossed with homozygous dwarf plant, the offspring will be
If a homozygous red flowered plant is crossed with a homozygous white flowered plant, the off springs would be
Pure line breed refers to ____.
In humans, attached earlobes are a dominant feature over free earlobes while hypertrichosis of the ear is a holandric (-linked) feature. A man with attached earlobes and extensive hair on pinna married a woman having free earlobes. The couple had one son with attached earlobes and hairy pinna, another son with free earlobes and hairy pinna and two daughters with attached earlobes. One of the daughters married a man with free earlobes and sparse hair on pinna. They had two sons. What would be the characteristics of their pinnae? What would be characteristic of their two daughters?
In the given pedigree, circles represent females and squares represent males. Filled shapes indicate affected individuals; while, unfilled shapes indicate unaffected individuals for a particular disease controlled by gene .
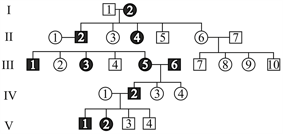
i. linked dominant
ii. Autosomal dominant
iii. Autosomal recessive
iv. The genotype of is or
v. The genotypes of and are same for the trait
vi. The genotype of is or
Analyse the inheritance pattern along with the genotype is dominant allele and is recessive allele) and choose the correct options(s).
A sex-linked recessive gene in humans produces color-blind men when hemizygous , and color-blind women when homozygous . A non-linked, autosomal, but sex-influenced gene for pattern baldness is dominant in men (BB or Bb) and is only manifested in women when they are homozygous dominant (BB). A heterozygous bald, color-blind man marries a non-bald woman with normal vision whose father was non-bald and color-blind and whose mother was bald with normal vision. Choose the correct option(s) for the phenotypic expectations for their children.
In a plant, red flower colour is dominant over white, tall stem is dominant over dwarf and round seed shape is dominant over wrinkled. A plant that is heterozygous for all three characters was allowed to self-fertilize. What is the proportion of the offspring expected to be homozygous for red flower colour, homozygous for tall stem and heterozygous for seed shape?
In the given pedigree, circles represent females and squares represent males. Filled shapes indicate affected individuals; while, unfilled shapes indicate unaffected individuals for a particular disease controlled by gene .
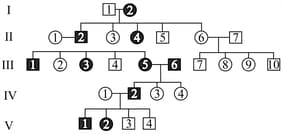
i. linked dominant
ii. Autosomal dominant
iii. Autosomal recessive
iv. The genotype of is or
v. The genotypes of and are same for the trait
vi. The genotype of is or
Analyse the inheritance pattern along with the genotype is dominant allele and is recessive allele) and choose the correct options(s).
The pathway that determines skin pigmentation in dogs is governed by two unlinked genes (I and II). While gene, I determine the type of pigment, gene II is responsible for its deposition in skin cells. Allele (gene I) results in a black pigment; whereas, p produces a brown pigment. While allele Q (gene ) results in the deposition of pigment, q will not allow the same. Alleles P and Q are dominant over p and q, respectively. Lack of pigment deposition results in an albino phenotype. When two canines with genotype PpQq are mated, the phenotypic ratios of offspring would be
A crop variety was developed at a research station in Dehradun (located in a temperate zone) and this variety produces round ( or ) or wrinkled seeds with green ( or ) or yellow seed colour. A field test was performed with seeds from a cross between (round and green) and (wrinkled and yellow) parents. Seeds obtained from this test were planted at the same research station and compared to three new tropical locations with different levels of microbial infection and salinity challenges.
| Temperate region | Tropical region | Tropical region with microbial infection | Tropical region with microbial infection and high salinity | |
| Number of seeds sown | 800 | 800 | 800 | 800 |
| Number of seeds germinated | 795 | 355 | 210 | 190 |
| Number of plats reached flowering | 775 | 350 | 208 | 48 |
| Number of plants produced seeds | 766 | 345 | 204 | 47 |
| Total yield | 8.2 Kg (6.2 Kg Green + 2.0 Kg Yellow) | 3.6 Kg (1.5 Kg Green + 2.1 Kg Yellow) | 2.1 Kg (0.05 Kg Green + 2.05 Kg Yellow) | 0.51 Kg (0.01 Kg Green + 0.5 Kg Yellow) |
Based on the information provided and assuming that the genes follow Mendelian inheritance (with no other factors affecting the yield), choose the correct statement(s) from the options given below.
A cross was performed between two parent plants of unknown genotypes. The offspring were segregated based on two flower characteristics i.e. flower colour [magenta or white] and flower position [axillary or terminal] and counted. The two genes responsible for these characters are not linked and segregate independently. Based on the information given in the table, predict the genotypes of the parents.
| phenotype | magenta and axillary | magenta and terminal | white and axillary | white and terminal |
| number of offspring |
